Behind Our Designs—Victory or Death
“Victory or Death” was the countersign for the troops for the attack on Trenton on Christmas Day night, December 25–26, 1776.
During a “violent storm of rain, hail, and snow,” more than 2,400 soldiers,18 cannons, and 75-100 horses crossed the Delaware. Their attack was a complete surprise.
The Americans captured 896 Hessians and killed 22. (And no, the Hessians weren’t drunk.) Three Americans were killed and six wounded, including a near-fatal wound to future president James Monroe.
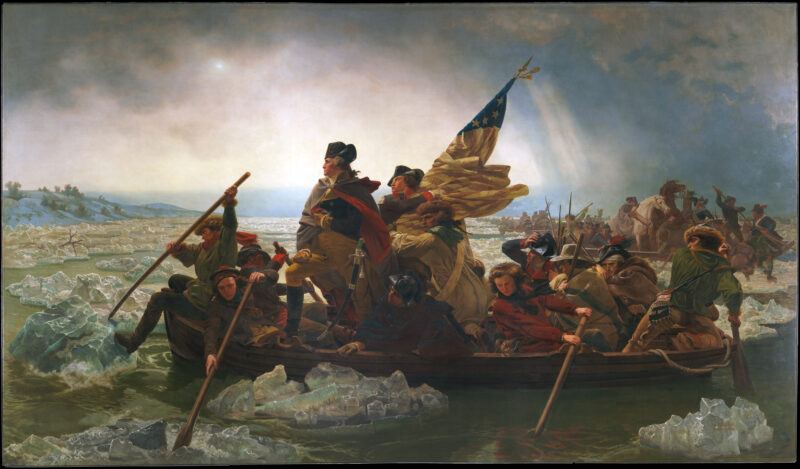

Washington Crossing the Delaware by Emanuel Leutze German American, 1851 (The Metropolitan Museum of Art, https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/11417)
Earlier in the month, Benjamin Rush, Philadelphia physician, member of the Continental Congress and signer of the Declaration of Independence, visited Washington four miles from the Delaware River and later wrote:
“He appeared much depressed and lamented the ragged and dissolving state of his army in affecting terms. I gave him assurances of the disposition of Congress to support him, under his present difficulties and distresses. While I was talking to him I observed him to play with his pen and ink upon several pieces of paper. One of them by accident fell upon the floor near my feet. I was struck with the inscription upon it. It was “victory or death.”
Washington surely knew what was at stake. Enlistment for most men was to expire December 31st.
His daring raid succeeded.
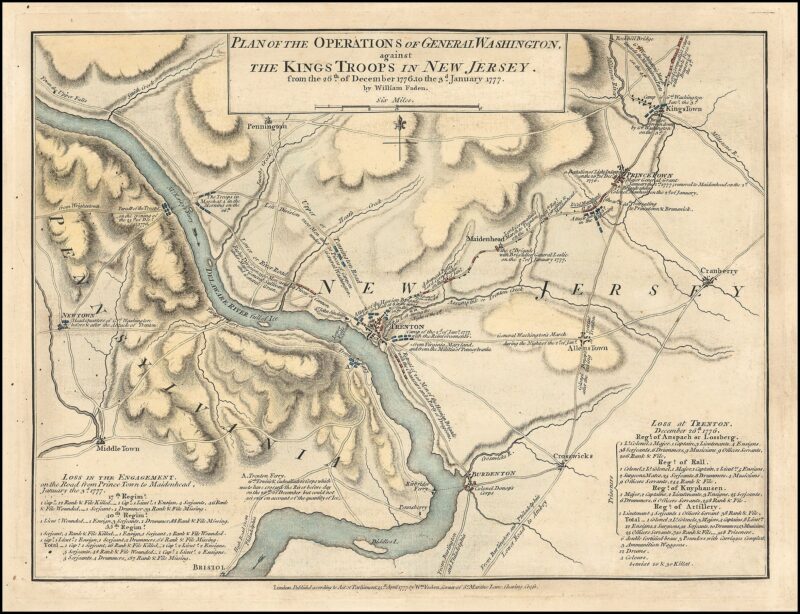
A map of the Delaware River area depicting the route George Washington and his Army made during the crossing, by William Faden, an English cartographer and a publisher of maps. He printed the North American Atlas in 1777, and ". . . it became the most important atlas chronicling the Revolution's battles." There were 29 maps in the atlas, and they included detailed battle maps drawn by eyewitnesses. Source: Wikipedia (large image of the map) By William Faden - Library of Congress, Public Domain













